Our built environments offer shelter and comfort, but within the walls and beneath the floors can lurk an unseen enemy – mould. While often associated with damp basements or leaky roofs, mould can also find a breeding ground within the very materials used to construct our homes and buildings. Understanding how building materials can contribute to mould growth is crucial for maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
Susceptible Materials:
Not all building materials are created equal when it comes to mould resistance. Here’s why some materials are more susceptible:
- Porous Materials: Materials like drywall, wood, and cellulose insulation readily absorb moisture, creating a welcoming environment for mould spores.
- Organic Materials: Natural materials like wood, cork, and bamboo inherently contain organic matter that serves as a food source for mould.
- Materials with Low Permeability: Materials like vinyl and certain paints may trap moisture within walls or beneath surfaces, promoting mould growth.
Contributing Factors:
Beyond the inherent properties of building materials, several factors can contribute to mould growth:
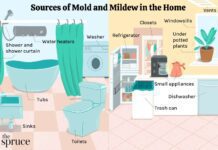
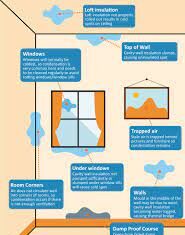
- Moisture Intrusion: Leaks from roofs, plumbing, or condensation can introduce excess moisture into walls and building materials.
- Poor Ventilation: Inadequate ventilation allows moisture to accumulate, creating a humid environment ideal for mould.
- Construction Defects: Improper construction techniques or faulty building materials can lead to trapped moisture and potential mould growth.
- Temperature Extremes: Consistent cold or hot temperatures can create condensation and promote mould growth.
Signs of Mold Infestation:
Identifying a potential mould problem requires a keen eye and awareness:
- Visible Mold Growth: Look for fuzzy patches on walls, ceilings, floors, or behind furniture, often appearing in various colours like black, green, or white.
- Musty Odors: A persistent musty or earthy smell can be a telltale sign of mould growth.
- Health Concerns: If you experience allergy-like symptoms like coughing, sneezing, or difficulty breathing, especially after spending time indoors, it could be mould-related.
Protecting Your Built Environment:
Several practices can help prevent mould growth in your building materials:
- Address Moisture Issues: Promptly address any leaks or sources of moisture intrusion.
- Maintain Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation throughout your home or building to prevent moisture build-up.
- Choose Mold-Resistant Materials: When opting for building materials, consider mould-resistant options, especially in high-moisture areas like bathrooms and kitchens.
- Maintain a Healthy Indoor Humidity Level: Aim for indoor humidity levels between 30% and 50% to minimize condensation.
- Regularly Inspect for Mold: Regularly inspect potential mould breeding grounds like attics, basements, and crawl spaces.
Taking Action for a Healthy Home:
By understanding how building materials can contribute to mould growth and implementing preventative measures, you can create a healthy and comfortable living environment. If you suspect a mould problem, consult a qualified professional for assessment and remediation. Remember, early detection and action are crucial to preventing further damage and safeguarding your health and well-being.