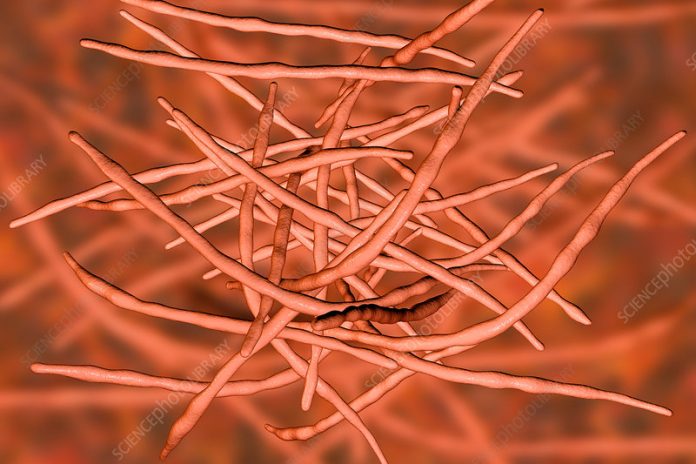
Actinomycetes are a unique group of bacteria that look and behave a bit differently from most other bacteria. Instead of being just simple, round or rod-shaped cells, actinomycetes grow long, branching filaments—kind of like tiny bacterial “roots” spreading out in the soil. These networks, called mycelia, can even look similar to the threads that fungi grow (even though actinomycetes are definitely bacteria, not fungi).
You’ll often find actinomycetes in soil and water. They’re super important for breaking down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the environment, and even creating the well-known earthy smell you notice after rain (thanks to a compound called geosmin that they produce). On top of that, actinomycetes—especially members of the Streptomyces group—are behind many antibiotics and medicines that we use to fight infections.
Relationship to Cyanobacteria:
- Actinomycetes and cyanobacteria are both bacteria, but they’re from very different families. Actinomycetes belong to a group called Actinobacteria, known for growing in soils and making antibiotics. Cyanobacteria, on the other hand, are sometimes called “blue-green algae,” and they use sunlight to make their own food, like plants, often living in aquatic environments.
- What they have in common: Both groups can produce some of the same earthy or musty-smelling compounds (such as geosmin) which can affect the taste and smell of water or soil.
- Differences: Cyanobacteria are famous for forming “algal blooms” in water and can sometimes create toxins that are harmful. Actinomycetes, while important for soil health and medicine, usually aren’t toxic and don’t form blooms the way cyanobacteria do.
- In nature, both groups often co-exist in soils and water, and sometimes researchers study both at the same time when investigating taste, odor, or environmental changes.
In summary: Actinomycetes are soil-loving, filament-forming bacteria that are serious powerhouses for breaking down stuff in nature and making antibiotics, while cyanobacteria are photosynthetic bacteria living in water. They’re not closely related but can both impact our environment in interesting ways, especially when it comes to those earthy smells and water ecosystems.